Green Energy
From Bikyamasr:
HAMBURG IS THE EPICENTER OF THE DEADLIEST E. COLI OUTBREAK IN MODERN HISTORY"
“It’s quite possible that there’s a crazy person out there who thinks 'I’ll kill a few people or give 10,000 people diarrhoea’. It’s a negligent mistake not to investigate in that direction.”
For anyone who does not remember, Hamburg is the city of Mohammed Atta. And, after 9/11, it was reported that Hamburg was a home to over 1,000 "Islamic Radicals".
MORE FROM WILL AT THE OTHER NEWS, VIA THE TELEGRAPH:
- New Virus Originated In The Middle East
A bit of a medical mystery and a deadly one: A mysterious new respiratory virus that originated in the Middle East spreads easily between people and appears more deadly than SARS, doctors reported Wednesday after investigating the biggest outbreak in...
- German E Coli Contains Bubonic Plague Dna?
According to this May 21, 2011 article in Spiegel Online International: ...On Tuesday, the German newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung reported that Karch [the director of the RKI's EHEC consulting laboratory at the Münster University Hospital in western...
-
Enterohaemorrhagic E. coli, or EHEC - 'A Totally New Disease Pattern' From Spiegel via Will at The Other News: Doctors Shaken By Outbreak's Neurological Devastation. The patient at the Hamburg-Eilbek Hospital describes to doctors how she...
- Bioengineered E Coli?
(With a hat tip to 12iggymom) Please tell me that THIS isn't possible. Excerpt: Forensic evidence emerges that European e.coli superbug was bioengineered to produce human fatalities ...There's really only one way this happens (and only one way)...
- Hmm ... "hamburg Is The Epicenter Of The Deadliest E. Coli Outbreak In Modern History"
“It’s quite possible that there’s a crazy person out there who thinks 'I’ll kill a few people or give 10,000 people diarrhoea’. It’s a negligent mistake not to investigate in that direction.” For anyone who does not remember, Hamburg...
Green Energy
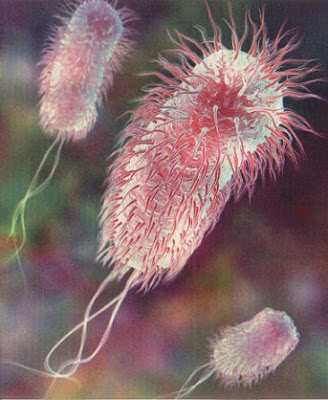
Egypt likely responsible for Europe’s E. coli outbreak

From Bikyamasr:
CAIRO: European investigators on Tuesday said that one shipment of fenugreek seeds from Egypt is the likely culprit for the E. coli outbreak in Germany that has already killed 49 people and led to a smaller outbreak in neighboring France.Remember, here at IBA, we have shown you that:
According to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), additional European Union countries may have imported tainted seeds and called on the European Commission to make “all efforts” to prevent any further consumer exposure.
Consumers should not eat sprouts or sprouted seeds unless they are thoroughly cooked, a statement from the EFSA said.
Some 4,000 people in Europe and North America have been infected in two outbreaks of E. coli infection – one centered in northern Germany and one focused around the French city of Bordeaux.
Almost all of those affected in the first outbreak – the deadliest on record – lived in Germany or had recently traveled there. The infection has killed 48 people in Germany and one person in Sweden.
“The analysis of information from the French and German outbreaks leads to the conclusion that an imported lot of fenugreek seeds which was used to grow sprouts imported from Egypt by a German importer is the most common likely link,” the EFSA said in a statement.
It added that the contamination of the seeds with a highly toxic strain of E. coli had taken place “at some point prior to leaving the importer.”
HAMBURG IS THE EPICENTER OF THE DEADLIEST E. COLI OUTBREAK IN MODERN HISTORY"
“It’s quite possible that there’s a crazy person out there who thinks 'I’ll kill a few people or give 10,000 people diarrhoea’. It’s a negligent mistake not to investigate in that direction.”
For anyone who does not remember, Hamburg is the city of Mohammed Atta. And, after 9/11, it was reported that Hamburg was a home to over 1,000 "Islamic Radicals".
German E Coli Contains Bubonic Plague DNA?
German authorities are investigating ‘a possible deliberate act’ as search for source of E. coli outbreak continues
An outbreak of killer E. coli that has spread to 12 countries and killed 19 people may be linked to a Hamburg festival in May and could have claimed a 20th victim, reports said on Saturday.
German weekly newspaper Focus said authorities were looking closely at a harbour festival that took place in Hamburg on May 6-8 and that drew 1.5 million visitors from Germany and abroad.
The newspaper noted that the first reported case of E. coli infection followed just a week later in the city’s university hospital.
Germany’s national disease institute The Robert-Koch Institute, however, said there did not appear to be a connection. “Press information regarding a link between the E. coli infections and large gatherings does not correspond with the institute’s knowledge,” German news agency DPA quoted it as saying.
Local media also said Saturday a man in his 50s who died in Brandenberg may be the 20th victim in Europe but the cause of death was uncertain because he had several other infections as well as E. coli.
The latest confirmed death was of an 80-year-old woman in the northern German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania on Friday.
The European Commission on Saturday said it was preparing to send a team of experts to Germany to help speed up efforts to locate the source of the outbreak, a statement said.
So far, scientific tests have failed to support a link to the epidemic, the European Union’s Reference Laboratory for E. coli in Rome has said.
Faced with the mystery, German reports said police were investigating a possible deliberate act and were also checking two restaurants in the northern town of Lubeck, one in which 17 diners fell ill and another in which eight women were affected, one of whom died.
MORE FROM WILL AT THE OTHER NEWS, VIA THE TELEGRAPH:
The warning from the Centre for the Protection of National Infrastructure [CPNI], which operates as part of the Security Service, comes as experts warned the deadly E.coli outbreak in Germany has highlighted the vulnerability of the food chain and how quickly bacteria can spread.The highly virulent strain has claimed 18 lives and left more than 1,800 seriously ill, with the true number of cases expected to be far higher.A senior German doctor last night called for an investigation into the possibility that the bacteria had been spread deliberately.Klaus-Dieter Zastrow, chief doctor for hygiene at Berlin’s Vivantes hospital, said:
“It’s quite possible that there’s a crazy person out there who thinks 'I’ll kill a few people or give 10,000 people diarrhoea’. It’s a negligent mistake not to investigate in that direction.”
- New Virus Originated In The Middle East
A bit of a medical mystery and a deadly one: A mysterious new respiratory virus that originated in the Middle East spreads easily between people and appears more deadly than SARS, doctors reported Wednesday after investigating the biggest outbreak in...
- German E Coli Contains Bubonic Plague Dna?
According to this May 21, 2011 article in Spiegel Online International: ...On Tuesday, the German newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung reported that Karch [the director of the RKI's EHEC consulting laboratory at the Münster University Hospital in western...
-
Enterohaemorrhagic E. coli, or EHEC - 'A Totally New Disease Pattern' From Spiegel via Will at The Other News: Doctors Shaken By Outbreak's Neurological Devastation. The patient at the Hamburg-Eilbek Hospital describes to doctors how she...
- Bioengineered E Coli?
(With a hat tip to 12iggymom) Please tell me that THIS isn't possible. Excerpt: Forensic evidence emerges that European e.coli superbug was bioengineered to produce human fatalities ...There's really only one way this happens (and only one way)...
- Hmm ... "hamburg Is The Epicenter Of The Deadliest E. Coli Outbreak In Modern History"
“It’s quite possible that there’s a crazy person out there who thinks 'I’ll kill a few people or give 10,000 people diarrhoea’. It’s a negligent mistake not to investigate in that direction.” For anyone who does not remember, Hamburg...
