Green Energy

- Geothermal Energy The Power From Below!
"Geothermal" is from two Greek words – "geo" meaning the earth and "therme" meaning heat. "Energy" stems from the Greek word "ergon" - meaning work. Literally translated, geothermal energy is "the work of earth's heat".So what is geo-energy...
- How A Wind Turbine Works
Let's Take A Look At How A Wind Turbine WorksThe easiest way to understand how a wind turbine works is to think of a fan operating in reverse.So instead of electricity spinning the blades to generate wind, the wind spins the blades to generate electricity!A...
- Solar Energy: The Energy That Comes From Outer Space
Solar energy is a clean energy as it generates neither greenhouse gas emissions nor pollution. Today, solar energy represents less than 1% of all energy produced by humans and Germany is the country that produces the most. There are two technologies for...
- Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is the heat from the Earth. It's clean and sustainable. Resources of geothermal energy range from the shallow ground to hot water and hot rock found a few miles beneath the Earth's surface, and down even deeper to the extremely...
- Ocean Energy
The ocean can produce two types of energy: thermal energy from the sun's heat, and mechanical energy from the tides and waves. Oceans cover more than 70% of Earth's surface, making them the world's largest solar collectors. The sun's...
Green Energy
Hybrid Power Generation Systems
Combined Heat and Power (CHP)
Combined Heat and Power (CHP) is the simultaneous generation of usable heat and power (usually electricity) in a single process. CHP plants enable the recovery of waste heat and / or better overall utilisation of the heat energy supplied to the system. They can thus be highly energy efficient.
CHP units may be characterised by their design priorities
- Heat Utilisation - Using surplus heat from another heating process to generate electricity.
- Heat Recovery - Making use of the waste heat resulting from electricity generation.
- Internal Combustion Engine Systems
- Back Pressure Steam Turbines
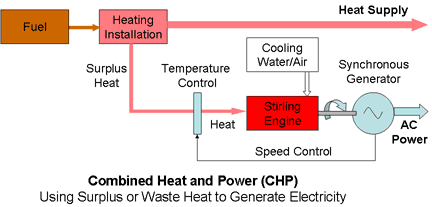
Small scale or Micro-CHP installations are now becoming available for home use. The standard domestic heating boiler is replaced by a heating unit which also provides the heat to power a Stirling Engine which in turn drives an electrical generator.
The heating unit in the CHP plant must be dimensioned to provide sufficient surplus heat to power the Stirling engine. Using a single heating unit for both the heat and power generation simplifies the design and permits economies of scale.
Furthermore generating electricity in small local installations avoids the energy losses incurred in the transmission grid.
CHP can use a variety of fuels and heating technologies, however the majority of small CHP plants tend to be fuelled by natural gas.
More information on domestic electricity generation can be found in the section on Small Scale Systems.
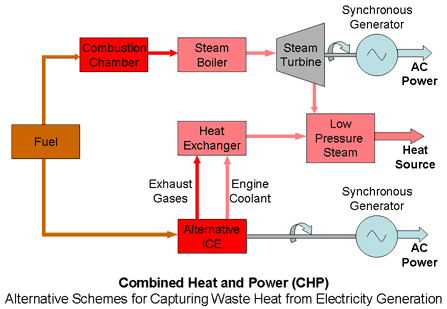
Approximately 60-70% of the total energy input is converted to heat that can be recovered from the engine exhaust and jacket coolant, while smaller amounts are also available from the lube oil cooler and the turbocharger's inter cooler and after cooler (if so equipped).
Larger scale CHP units recover the steam and hot water produced in conventional electricity generating plants for further use in industrial processes or community and space heating. Two systems are shown in the above diagram.
Normally the exhaust steam from turbines used for generating electricity passes through a condenser to maximise the energy extracted from the steam. If heat for industrial or other processes is required, a different configuration known as a back pressure steam turbine is used. Instead of passing through a condenser the exhaust steam at "overpressure", slightly over atmospheric pressure, is directed to the desired heating or auxiliary mechanical systems.
Overall efficiencies up to about 60% are possible but the difficulty of finding a practical use for the surplus heat sets a limit to the size of these systems.
See also Fuel Cell CHP
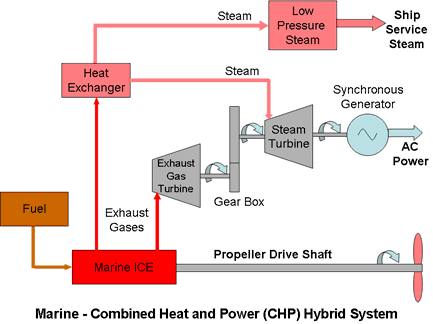
Hybrid System for Large Marine Applications
The most powerful and one of the most efficient prime-movers in the world today (2008) is the Wartsila-Sulzer 14 cylinder turbo charged two-stroke diesel engine, designed for powering very large container ships.

The cylinder bore is 960 mm (38 inches) and the stroke is 2500 mm (98 inches) providing a capacity of 25,337 litres (1,546,165 cu ins) and a continuous output power of 80,080 kW (108,920 bhp) or 4.27 bhp/litre at 102 rpm with an overall efficiency of around 52%. The engine is 27.3 m long and 13.5 m high with an overall weight of 2300 tonnes.
The engine's main output shaft drives the ship's propellers and exhaust gases from the engine pass through a heat exchanger to generate steam for a turbine-driven electricity generator. The turbo generator set also includes an exhaust-gas powered turbine driven by a portion of the exhaust gases diverted from the main flow through the engine's turbochargers. The power output from the generator is 9,860 KWe, about 12% of the main engine power. A portion of the steam from the exhaust economiser is also utilised in shipboard heating services.
Co-generation - Combined Cycle Power Generation
This is a special case of both heat recovery and heat utilisation in which the heat recovered from one electricity generating process is used to generate electricity in a different process.

Hybrid systems using waste heat from a high capacity electricity generating plant can be used to power a subsidiary generator.
Gas turbine conversion efficiency improved from a maximum of around 40% to 60% by using waste heat to produce heat to drive a steam turbine.
this arrangement is also used with very large internal combustion engined generators.
See also Gas Turbines and Steam Turbine Electricity Generating Plants
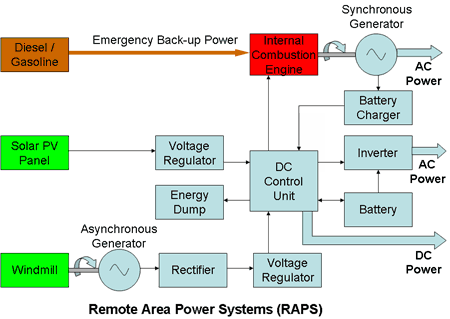
Remote Area Power Systems (RAPS)
When considering a remote stand alone electrical power generating system it makes economic sense to specify a hybrid system with both solar and wind power systems together rather than a single energy source.

Hybrid systems have the following advantages:
- The systems are complementary. During the summer months when there's not much wind there should be ample sunlight and during the dark winter months it is usually quite windy.
- Two different energy sources provide a diversity of supply, reducing the risk of power outages.
- High cost ancillary equipment such as the battery and the inverter required for a single system must be specified to carry the full system load. A second system can thus be added without increasing its capacity or adding cost for more of these components.
- Because of the supply diversity, the capacity of the battery can most likely be reduced.
- The required generating capacity of the basic solar and wind energy conversion units can be reduced since the total load is shared.
A stand alone system will often incorporate a small stand-by diesel generating set to supply critical loads in case of an emergency.
Coordination of the different energy sources is managed by a DC control unit which has the following functions
- Accepts the DC power from the three generating units according to priority rules
- Controls the power delivery to the load or loads
- Monitors the battery voltage and charges the battery as required.
- Cuts off the charger when the battery is fully charged and diverts the power to a suitable load
See also Generators
Return to Electrical Energy Supply Overview
- Geothermal Energy The Power From Below!
"Geothermal" is from two Greek words – "geo" meaning the earth and "therme" meaning heat. "Energy" stems from the Greek word "ergon" - meaning work. Literally translated, geothermal energy is "the work of earth's heat".So what is geo-energy...
- How A Wind Turbine Works
Let's Take A Look At How A Wind Turbine WorksThe easiest way to understand how a wind turbine works is to think of a fan operating in reverse.So instead of electricity spinning the blades to generate wind, the wind spins the blades to generate electricity!A...
- Solar Energy: The Energy That Comes From Outer Space
Solar energy is a clean energy as it generates neither greenhouse gas emissions nor pollution. Today, solar energy represents less than 1% of all energy produced by humans and Germany is the country that produces the most. There are two technologies for...
- Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is the heat from the Earth. It's clean and sustainable. Resources of geothermal energy range from the shallow ground to hot water and hot rock found a few miles beneath the Earth's surface, and down even deeper to the extremely...
- Ocean Energy
The ocean can produce two types of energy: thermal energy from the sun's heat, and mechanical energy from the tides and waves. Oceans cover more than 70% of Earth's surface, making them the world's largest solar collectors. The sun's...
